|
| |
Electrolyte
Definition of electrolyte: An aqueous solution containing dissolved
ions that result from the dissociation of salts.
!-------------------------------------------------------------!
$electrolyte
optional !
electrolyte-number
integer required !
electrolyte-region
double_array
required !
destination-directory character required
!
pH-value
double
required !
pH-value-sweep-active character optional !
pH-value-sweep-step-size double optional !
pH-value-sweep-number-of-steps integer optional !
electrolyte-equation
character
required !
extended-Poisson-Boltzmann
character
optional !
shift-PMF double optional !
shift-water-density double optional !
read-in-water-density-from-file
character
optional !
filename-water-density
character
optional !
local-dielectric-constant character
optional !
local-dielectric-constant-min-max
double_array
optional !
include-buffer character required !
buffer-name character optional !
buffer-concentration double optional !
pKa-temperature-dependence character optional !
pKa-ionic-strength-dependence character optional !
pKa-spatial-dependence character optional !
$end_electrolyte optional
!
!-------------------------------------------------------------!
Syntax
electrolyte-number =
1
=
2
=
integer
So far
only one electrolyte region is implemented.
-
electrolyte-region =
100d0 2000d0 ! [nm]
refers to region where the electrolyte/buffer has to be applied to, e.g.
from 100 nm to 2000 nm in 1D (xmin xmax)
- 1D simulation: xmin xmax
- 2D simulation: xmin xmax ymin ymax
-
3D simulation: xmin xmax ymin ymax zmin zmax
destination-directory = electrolyte/
Name of directory to which the files should be written. Must exist and
directory name has to include the slash (\ for DOS and / for UNIX).
pH-value =
0d0 ! pH = -lg(H+
concentration) = 11 -> concentration in [M]=[mol/l]
=
1d0 ! (strong
acid)
=
... !
=
6.5d0 !
=
7d0 !
=
... !
=
14d0 !
The pH value must be within the range 0 <= pH <= 14.
The concentration of the ions in the electrolyte is
relevant for the site-binding model and is given in units of [M]=[mol/l].
Note: The pH value that is specified here generates automatically the
relevant concentrations of H3O+ and OH-
ions (and their corresponding anion and cation counterparts, i.e. conjugate
base and conjugate acid). For details, see
$electrolyte-ion-content.
pH-value-sweep-active
= no
! (default)
The Poisson-Boltzmann equation is solved only
!
for the pH value specified in pH-value.
!
pH-value-sweep-active
= yes
!
The Poisson-Boltzmann equation is solved several times, starting
!
from the pH value specified in pH-value, then
pH-value-sweep-step-size =
0.5d0 !
pH-value-sweep-number-of-steps = 14
!
! For each pH value the relevant output is written out,
! labelled by 'ind000.dat', 'ind001.dat', 'ind002.dat',
...
! Note: The total range of allowed sweeps must be within the range 0
< pH < 14.
electrolyte-equation =
Poisson-Boltzmann
! Poisson-Boltzmann equation
= Debye-Hueckel-approximation ! Debye-Hückel approximation
= Stern-Grahame-model
! Stern-Grahame model (not implemented yet)
The Debye-Hückel (DH) approximation in the
linearized form of the nonlinear Poisson-Boltzmann equation and is valid only for
zi e (phi(x) - UG) < kBT, i.e. at
room temperature and for UG = 0 V, zi e phi(x)
should be smaller than 25 meV.
- i : ion-number
(For details, see $electrolyte-ion-content.)
-
ion-valency (For details, see
$electrolyte-ion-content.)
-
- phi: electrostatic potential in [V]
- UG: applied gate voltage in [V]
The Debye-Hückel approximation yields a limiting result to which general
solutions must converge for small potentials. Particularly in the limit of
zero ion concentrations the solution of DH becomes exact.
For more information on these three models, have a look into the diploma
theses of Michael Bayer and Christian Uhl, or the PhD thesis of Sebastian
Luber.
extended-Poisson-Boltzmann = no
! (default)
= PMF !
PMF hydrophilic
or hydrophobic local dielectric
constant, see next specifier.
==>
Hydrophobic/hydrophilic (i.e. nonpolar/polar) solid/liquid interfaces
-
local-dielectric-constant
= constant-water-density !
(default)
= hydrophobic
!
= hydrophilic
!
= hydrophobic-SAM
!
= hydrophilic-SAM
!
local-dielectric-constant-min-max = 1d0
78d0
!
By default, inside the electrolyte the water density is assumed to be
constant (constant-water-density).
Alternatively, at the solid/electrolyte interface the water density can be
assumed to vary locally:
- hydrophobic for a nonpolar surface
(i.e. repelling water)
- hydrophilic
Instead of assuming a constant value of approx. eps = ~ 80 for the
static dielectric constant of water,
one can assume a local dielectric constant eps(z)
of water based on eq. (2) of the following paper:
Reversed Anionic Hofmeister Series: The Interplay of
Surface Charge and Surface Polarity
N. Schwierz, D. Horinek, R. R. Netz
Langmuir
26, 7370 (2010)
This will lead to a spatial variation of the dielectric constant of the
electrolyte according to the following equation:
eps(z) = epsmin + ( epsmax - epsmin
) rho(z) / rho0
epsmax is the dielectric constant of water (epsmax =
78)
epsmin is the dielectric constant of e.g. vacuum (epsmax
= 1) (because there is a distance of a few Angstrom where there are no ions
at the solid/electrolyte interface) or a self-assembled monolayer (e.g. epsmin
= epsSAM = 4).
Here, the dielectric constant is assumed to be proportional to the water
density rho(z) where rho0 is the bulk density of water.
This density profile has been obtained by
molecular dynamics simulations approximated by a fit function (Schwierz et al.).
By using this fit function, we obtain the following figure for rho(z) / rho0
(solid/electrolyte interface at z = 0 nm):
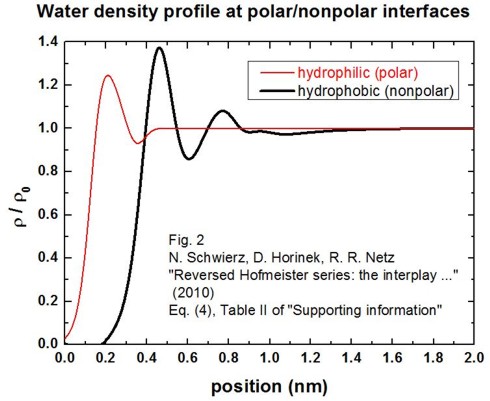
Note that the water is depleted from the interface in the hydrophobic case by
about 0.4 nm.
This feature works for both boundaries of the electrolyte. This feature has
only been implemented/tested in 1D so far.
read-in-water-density-from-file = yes
filename-water-density = "\\Home\My
Documents\My nextnano input files\read_in_WaterDensityDiamond.dat"
A file for the water density profile can also be read in. The
data file should start at 0 nm (position of interface), the units are [nm],
and at 0 nm it should hold: rho/rho0 = 0.
Further away from the interface (> several nm), it should hold: rho/rho0
= 1.shift-PMF =
0.1d0 ! [nm] (default:
0d0)
A negative value of dz shifts towards the solid/liquid
interface.shift-water-density =
0.1d0 ! [nm] (default:
0d0)
A negative value of dz shifts towards the solid/liquid
interface.
Buffer solution
include-buffer =
no ! (default)
include-buffer =
yes !
buffer-name =
ACETATE !
=
HEPES !
=
TRIS !
=
MOPS !
=
PBS !
=
... !
$buffer-solutions
buffer-concentration =
10d-3 ! 10 mM of buffer
(The units are [M] = [mol/l] = [mole/liter] = 1d-3 [mol/cm³].)
include-buffer = yes),
then these ions must not be specified under the keyword
$electrolyte-ion-content.
Moreover, the names, the valencies and the total number of buffer ions are
taken from the entries in the database and included into the electrolyte
region automatically.
From the total buffer concentration (buffer-concentration =
10d-3) the program internally calculates
the concentration of each buffer ion species self-consistently, taking into
account
- the pH value (pH-value = ...)
- the ionic strength (The pKa value depends
on the ionic strength: "modified pKa' value".)
- the temperature (The pKa value
depends on the temperature.)
Note that the constant 'A' that is used to calculate the
ionic strength dependence of the pKa value also depends on
the temperature.)
For details on 'A', see this keyword:
$buffer-constant-A(T)
For more details on these calculations, have a look at the keyword
$buffer-solutions.
pKa-temperature-dependence = yes !
(default) pKa' = pKa
+ dpKa/dT * DeltaT =
!
= pKa
+ dpKa/dT * (T -
298.15)
! where dpKa/dT is
the temperature coefficient specified in the database (dpKa_dT =
...)
!
= no
!
! Note: The temperature dependence of the constant
'A' that is used to calculate the ionic
! strength dependence of the pKa
value cannot be switch off.
! It can only fixed to a certain value,
independent of temperature, by specifying only one value
! of T and A(T) in the database
or in the input file.
pKa-ionic-strength-dependence = yes !
(default)
!
! This dependence can be described by an equation
(sometimes known as the
! Debye-Hückel relationship) where the constant A(T) enters.
! For details, see the description in the keyword
$buffer-constant-A(T).
= no ! The ionic
strength dependence of the pKa value is switched off.
-
pKa-spatial-dependence = yes !
(default)
! pKa-ionic-strength-dependence
but for each grid point.
! Generally, at each grid point, a different pH
value, i.e. concentration of [H3O+] ions, is possible.
! Thus, the ionic strength, the modified pKa'
value, the pH value and
! the concentration of the buffer ions is
determined self-consistently
! within the Poisson-Boltzmann equation in the
semiconductor/electrolyte system.
! The output of the spatially varying pH value, pKa'
value, and ionic strength is described below.
= no ! The same pKa'
value is assumed for all grid points.
Debye screening length
Information on the Debye screening length can be obtained from this file:
DebyeScreeningLength.txt
1/kappa = [
SUMi=1N [ epsilon epsilon0 kBT
/ (ci (zie)2) ] ]1/2
Example:
ion-number ion-valency ion-concentration
[mol/l] ion-name
1
-1.000000 7.0000002E-03
PBS^-
2 -2.000000
3.0000000E-03
PBS^2-
3 1.000000
1.3000000E-02
PBS+
4 -1.000000
2.0000001E-03
Cl-
5 2.000000
1.0000000E-03
Ni2+
6 -1.000000
0.1400000
Cl-
7 1.000000
0.1400000
K
8 1.000000
3.1622776E-08
H3O+
9 -1.000000
1.0000000E-06
OH-
10 -1.000000
3.1622776E-08
anion-
11 1.000000
1.0000000E-06
cation+
--------------------------------------------------------------------
dielectric constant: epsilon = 80.00000
====================================================================
Debye screening length: 1/kappa = 0.772540134486749 [nm]
====================================================================
Ionic strength
- Bulk ionic strength
Information on the (bulk) ionic strength can be obtained from this file:
IonicStrength.txt
I = 1/2 SUMi=1N (ci
zi2)
I = ionic strength in units of [ ] (or better:
[concentration] = [M])
i = number of ion species
N = total number of different ion species
ci = concentration of ion species 'i'
zi = charge of ion species 'i'
For details, see chapter 3 in
R.J. Beynon, J.S. Easterby, "Buffer solutions: The basics", Oxford University
Press (1996).
Example:
ion-number ion-valency ion-concentration
[mol/l] ion-name
1
-1.000000 1.0000000E-02
Cl-
2 1.000000
1.0000000E-02
Na+
3 1.000000
1.0000000E-07
H3O+
4 -1.000000
1.0000000E-07
OH-
5 -1.000000
1.0000000E-07
anion-
6 1.000000
1.0000000E-07
cation+
--------------------------------------------------------------------
====================================================================
Ionic strength: I = 1.000020000000000E-002 [M]
([M]= [mol/l])
====================================================================
- Spatially varying ionic strength
In addition, as the concentration of the ion species varies with the spatial
grid coordinate, the ionic strength as a function of position is printed out
into a file. Possible filenames are:
- IonicStrength_vs_position1D.dat
(1D)
- IonicStrength_vs_position1D_ind001.dat
(1D)
- IonicStrength_vs_position2D.fld
/ *.coord / *.dat (2D/3D)
- IonicStrength_vs_position2D_ind004.fld / *.coord / *.dat
(2D/3D)
[nm], the second column contains the ionic strength for this grid
coordinate in units of [M].
At the grid point coordinates where the electrolyte's ion concentration is
identical to the bulk ion concentration, the ionic strength must be equal to
the bulk ionic strength which is printed out to the file
IonicStrength.txt. For further details on the bulk ionic strength, see
the description above.
- Spatially varying pH value and modified pKa'
value
The files
- pH_vs_position1D/2D/3D.dat
- pKa_vs_position1D/2D/3D.dat
- pKa1_vs_position2D/3D.dat
contain the grid point dependent pH value (calculated
from the spatially varying H3O+ concentration) and the
grid point dependent modified pKa' value(s).
- Spatially varying concentration of buffer ions
The files
- BufferIonConc_vs_position1D.dat
- BufferIonConc1_vs_position2D/3D.dat
-
BufferIonConc2_vs_position2D/3D.dat
contain the grid point dependent
concentration of the buffer ions (calculated self-consistently from
the spatially varying pH value, ionic strength and modified pKa'
value(s)). Note that these concentrations do not represent the actual
concentration ci(r) of the buffer ions (see equation
below), they represent the concentration c0(r).
ci(r)
= c0(r) exp [ - ( zi
e ( phi(r) - UG ) ) / ( kB T ) ]
Buffer solution
Information on the properties of the buffer can be obtained from this file:
Buffer1D.dat
Example:
===================================================================
Buffer name: PBS
===================================================================
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Input quantities:
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Buffer concentration: [PBS] =
1.000000000000000E-002 [M]
pH value:
pH = 6.636000
Temperature: T
= 298.1500 [K], i.e.
25.00000 [C]
The pKa value depends on temperature 'T'.
The pKa value depends on ionic strength 'I'.
z_acid =
0.0000000000000 -1.0000000000000 -2.0000000000000
dpKa/dT =
0.0044000000000 -0.0028000000000 -0.0260000000000
pKa (25 C) = 2.1500000000000
7.2100000000000 12.3300000000000
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Calculated quantities:
-------------------------------------------------------------------
pKa (T) =
2.1500000000000 7.2100000000000 12.3300000000000
pKa'(T,I) = 2.0815978725534
7.0047936176601 11.9879893627668
A = 0.511400000000000
Note: A always depends on temperature.
Ionic strength: I = 2.599208084382508E-002
[M]
Concentration of buffer ions:
-----------------------------
ion-number ion-valency ion-concentration [mol/l]
ion-name
0
...
H3PO4
3
-1.000000 7.0038019E-03
H2PO4^-
4 -2.000000
2.9959893E-03
HPO4^2-
5 -3.000000
1.3321431E-08
PO4^3-
6
1.000000 1.2995820E-02
Na^+
The concentration of all ions (not only the buffer ions), the ionic strength,
as well as the pKa' value(s) as a function of pH are contained
in this file:
BufferIonConc_vs_pH1D.dat
Oxide/electrolyte interface states (interface charges, so-called
"site-binding model") can be specified here:
$interface-states
More information on the electrolyte liquid and the Poisson-Boltzmann equation:
$electrolyte-ion-content
Preliminary feature
- If we have one Dirichlet boundary condition only, then this Dirichlet
value is assigned to PhiInfinityV(1).
- If we have two Dirichlet boundary conditions, then the second Dirichlet
value is assigned to PhiInfinityV(1).
(This means we assume that the electrolyte is at the right side of a 1D
simulation.)
|